2.7. Gamma calculation¶
2.7.1. Goal and Perquisite:¶
In this advanced tutorial we will see how to compute the secopnd hyperpolarizability using a mixed Finite Field and Response scheme as proposed in this article. REF This tutorial do not go into much details and presents only the procedure.
You should be familiar to the standard command presented in the get started tutorial and the one presented in the optical property overview.
The file needed to run this tutorial are located at: Frog/Doc/Tutorial_files/Traj/Tutorial_files/Traj/Tuto_get_strated for the MD trajectory and Frog/Doc/Tutorial_files/Gamma_calculation for all the other documents.
2.7.2. Overview:¶
The goal is to compute the frequency dependent second hyperpolarizability which correct the first hyperpolarizability from an external weak and homogenous electrtostatic field: 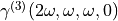 noted
noted 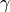 later on
later on
![\beta^{(2)}(2 \omega, \omega, \omega)[\bold{e}] = \beta^{(2)}(2 \omega, \omega, \omega) + \gamma^{(3)} (2 \omega, \omega, \omega, 0) \cdot \bold{e}](../_images/math/97eadfa28c14b95a2266d56f4b343292e7ce6890.png)
Where  is the external electrostatic field,
is the external electrostatic field, ![\beta^{(2)}(2 \omega, \omega, \omega)[\bold{e}]](../_images/math/d2f5436783f346227ee471c8d74a453fecbb5e03.png) the first hyperpolarizability in the presence of this external field and
the first hyperpolarizability in the presence of this external field and 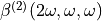 without.
without.
Note
Here the optical frequency 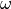 can be none-zero.
can be none-zero.
To compute this corrective term, we will used a Finite Field (FF) approach.
Several ![\beta^{(2)}(2 \omega, \omega, \omega)[\bold{e}]](../_images/math/d2f5436783f346227ee471c8d74a453fecbb5e03.png) is computed for increasing field in all the direction.
Then, a linear fit is performed to obtained
is computed for increasing field in all the direction.
Then, a linear fit is performed to obtained 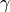 .
.
2.7.3. One Parameter file:¶
The key to achieve this is to compute the first hyperpolarizability (in the vacuum or in an electrostatic environement) with an extra homogenous electrostatic field. To do so, use the attribute qmparameter.static_electric_field and qmparameter.static_electric_field_direction:
qmparameter.static_electric_field = [0, 0, 0.001] # in atomic units
qmparameter.static_electric_field_direction = 'Laboratory' #Laboratory or Molecular
This will add an sptialy-homogeneous electrostatic field in the QM box along the laboratory direction with value (0, 0, 0.001) in atomic units.
 will creat the usual
will creat the usual  file with this extra electrostatic field.
Then, you should perform the QM calculation where the ground state is obtimized with this field and the first hyperpolarizability is extracted.
file with this extra electrostatic field.
Then, you should perform the QM calculation where the ground state is obtimized with this field and the first hyperpolarizability is extracted.
Note
Adding an extra electrostatic field is compatible with the PE scheme available in  , including the long-range decomposition.
, including the long-range decomposition.
Appart from this parameter, no changes should be made in the parameter file.
2.7.4. Procedure:¶
For a single parameter file (i.e. value of extra electrostatic field), you should not experience any differences compare to other  run.
However, to get the second hyperpolarizability, several run should be performed.
To do so, you can use the scripts: to_creat_gamma.sh.
It will generated automatically several directory for several extra electrostatic field.
In each directory should should run
run.
However, to get the second hyperpolarizability, several run should be performed.
To do so, you can use the scripts: to_creat_gamma.sh.
It will generated automatically several directory for several extra electrostatic field.
In each directory should should run  and perform the QM calculation.
and perform the QM calculation.
Note
You can further automatize this procedure by sending the  run automatically with a bit of bash writting, for instance see to_creat_gamma.sh. However keep in mind to test the procedure for a single extra field before!
run automatically with a bit of bash writting, for instance see to_creat_gamma.sh. However keep in mind to test the procedure for a single extra field before!
Finally, you can load all of the results and perform linear fit to obtained the second hyperpolarizability. An example is given as jupyter notebook. Note that this file can not be tested if you have not performed the QM calculations, see example_gamma_post_prod.ipynb.
